How to design a GOOD internal antenna? We list the 10 brief internal antenna design guidelines for your reference.
In any radio communication device, there is always an apparatus that radiates electromagnetic energy to space and receives electromagnetic energy from space. This device is an antenna.
The action of the antenna is to transmit digital signals or analog signals that modulate the RF frequency to the space wireless channel or receive digital or analog signals that modulate from the spatial wireless channel.
The emission and reception of electromagnetic waves need to be farther than by means of an antenna. Very close distance, such as 10 meters, you can work without tangible antennas, circuit boards, wires, etc., there is a way to work.
The antenna has an internal antenna type an external antenna type, an antenna has omnidirectional antenna type and a directional antenna type. Select the appropriate antenna type according to the device.
A good antenna can bring good performance to the IoT device, smart terminals, and wireless equipment, how to design a good built-in antenna?
How to design a good internal antenna with the below features?
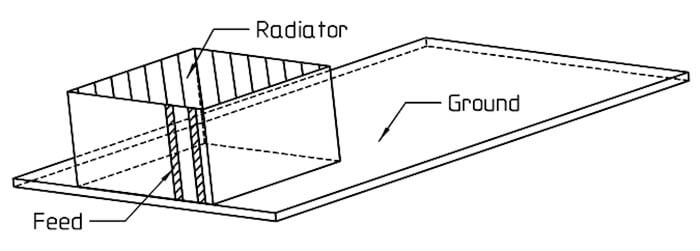
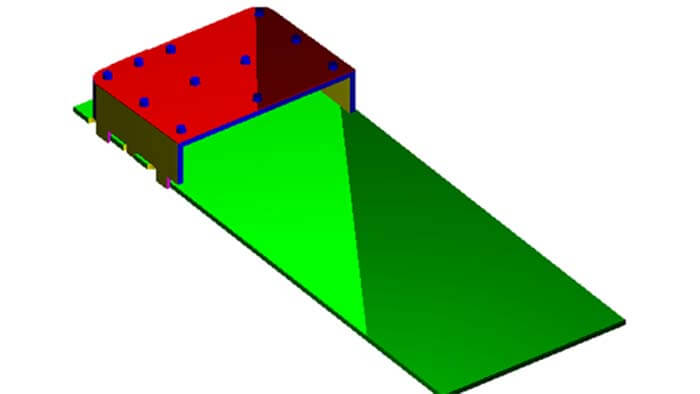
- Short circuited <=>l/4 resonator <=> compact structure
- Omnidirectional in a horizontal plane
- Co-and crosspolarisations
- Multiresonant
The 10 brief internal antenna design guidelines
Here we list the brief 10 internal antenna design guidelines for your reference.
- When designing any kind of small antenna for the mobile phone, it’s important to start designing the antenna TOGETHER with the antenna manufacturer in the very early stage to achieve the best possible performance, and when concerning internal antennas this is even MORE important.
- Use all space you have: BIG size is beautiful when concerning antenna’s performance
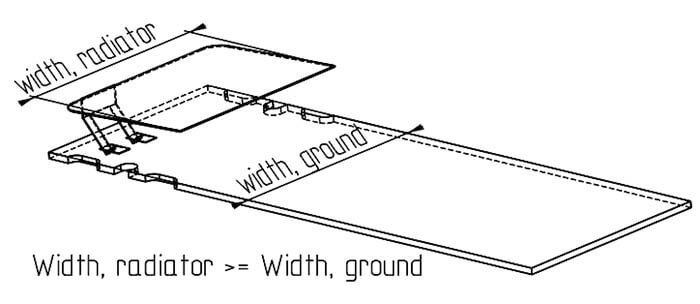
- Pay special attention to the antenna’s height (distance between radiator and ground) <=> BANDWIDTH!
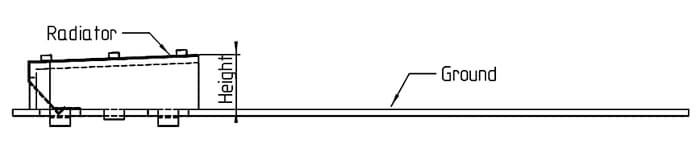
- Also, the length of the chassis has a remarkable effect on the performance of the antenna
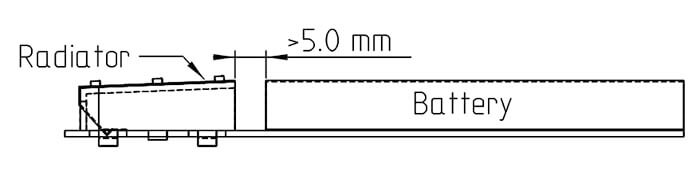
- Keep ALL metals as far as possible from the internal antenna, at least as far as the ground plane is 5mm.
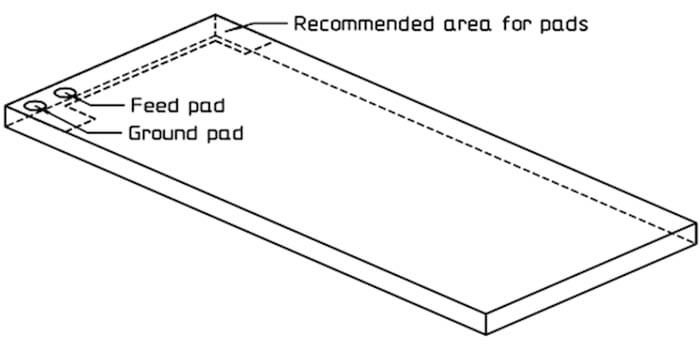
- Locate feeding and short-circuiting pads near the edge of the ground plane (phone’s PCB). For spring contacts the distance between bending point and PCB-pad should be 4 to 5 mm.
- Don’t shield pads or try to minimize shielding.
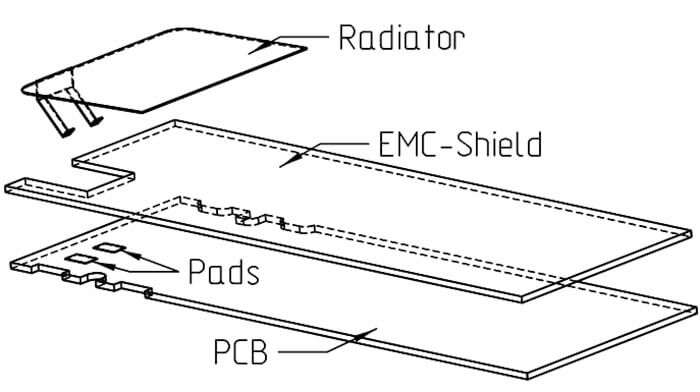
- Let the radiator’s edges have the free edge of the ground plane as much as possible, maybe even reach over the ground plane’s edge.
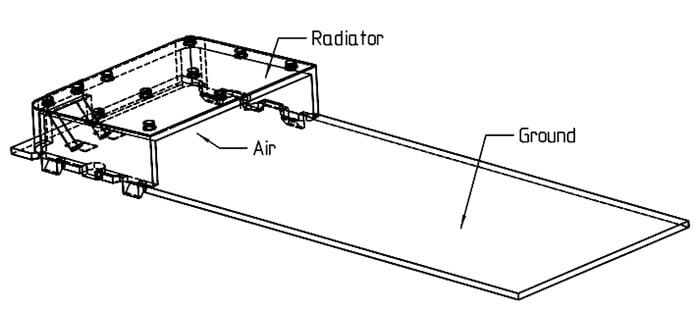
- All metals of the chassis have to be properly grounded to avoid power losses and additional non-radiating resonances. Pay special attention to RF-gaskets.
- Let the space between the radiator and ground plane be filled with air as much as possible, in other words, use as little support material as possible.
There are the 10 brief internal antenna design guidelines, we also have the FPC internal antenna design guidelines, EMI PCB Design Guidelines, EMC PCB Design Guidelines. If you still do not get the internal antenna design guidelines you need, please click here = Antenna design, It may help you.
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides the internal antenna design service with the PCB internal antenna design, FPC internal antenna design, spring internal antenna design, etc. Contact us for more design antenna details.
Besides the 10 Internal Antenna Design Guidelines article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G