The UAV’s transmission power EIRP has two frequency bands, 2.4G and 5G. What is the difference between the 2.4 G and 5G frequency bands, what are their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose 2.4G and 5G?
Usually, the frequency bands used by drones are public and open frequency bands (the Commission has divided the application of each frequency band), of course, there are many public frequency bands, such as Lora 433MHz, 900MHz, 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, etc., everyone can use, But it is necessary to control the transmission power, that is, each device has a maximum size limit, and it cannot be infinitely large, and it cannot be occupied by everyone.
In addition, there can also be devices with multiple different protocols in the same frequency band, such as the 2.4G frequency band, which can have ZigBee, Bluetooth, WiFi AP, and other devices.
The effective range of Bluetooth is about ten meters, the range of WiFi Access Point (router) is about one hundred and eighty meters, and ZigBee is very low data transmission and works intermittently.
Now we have to face a problem, that is, with the popularity of wireless devices, even if the transmission power of the device is controlled, there are still many devices with the same frequency in the same site, resulting in serious overlap of the site.
Your signal is useful to you, but it is useless to others, which is equivalent to causing interference and affecting the transmission of other people’s signals.
In the same way, other people’s equipment also affects the signal transmission of your equipment. This is one of the important reasons why UAVs fly close-in urban areas and far away in the suburbs or in the wild.
Why choose 2.4G and 5G?
Before that, let’s discuss the contents of the UAV system’s uplink and downlink transmissions. The information of the uplink (remote control to UAV) is mainly some control signals so that the UAV can fly according to the operator’s intention. , The amount of information transmitted on this link is relatively small, estimated to be several hundred k per second;
For the information on the downlink (drone to remote control), in addition to position information, flight status information, etc., the most important thing is image information. The first half of the information is not large, but the image information is huge, even if low resolution It is highly compressed, ranging from several megabytes to more than ten megabytes per second.
If the wireless frequency band is not wide enough, it will be difficult to display the return image smoothly. Generally, the higher the carrier frequency, the wider the frequency band specified in the agreement, so UAVs with video transmission will basically not use frequencies below 1GHz, but UAVs that do not require video transmission have relatively more frequencies to choose from.
China 2.4G and 5G frequency bands: 2.412 ~ 2.472 GHz 13 channels; 5.725 ~ 5.825 GHz 4 channels.
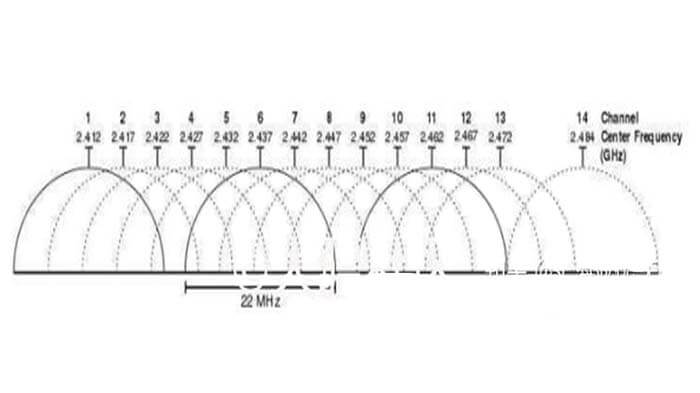
As can be seen from the above figure, the planned channel bandwidth is 22MHz, but the actual interval between each channel is 5MHz, which means that adjacent channels have overlapping frequency bands, which will inevitably affect signal transmission.
If everyone uses the same channel at the same time, and the distance is not far, then the transmission rate can be imagined. If three drone enthusiasts go to play together, the worst experience is to use the same channel, followed by adjacent channels. If you want to not affect each other, you can choose channels 1, 6, and 11. The 5GHz channels are independent of each other, each channel is 20MHz, and there is no overlap of frequency bands.
What are the characteristics of 2.4G and 5G frequencies?
Electromagnetic waves have wave-particle duality. The higher the frequency, the more obvious the particle characteristics, and the more like light; the lower the frequency, the more obvious the wave characteristics, and the more like sound waves.
The higher the frequency, the worse the ability of diffraction and diffraction, and at the same time, it is easier to attenuate, so the diffraction ability of 5.8G is worse than 2.4G.
If there are buildings or mountains between the drone and the remote control, the signal is basically difficult to pass.
For example, 2.4G has a certain degree of diffraction ability, and at the same time, it has a strong ability to penetrate walls. There is no problem with one wall, and a few more, the attenuation will be great. Another example is the rain and snow weather, the impact on 5.8G will be a little bit larger than 2.4G.
What is the impact of 2.4G and 5G different frequency bands on the antenna?
Frequency is the first factor that needs to be considered when designing an antenna. The biggest influence of frequency on an antenna is its size.
In addition, frequency bandwidth is also very important. The wider the frequency band, the larger the antenna volume and the greater the difficulty of the design, but as long as it meets the corresponding public open frequency band.
If it is 2.4G, as long as it includes 2.4G~2.4835GHz, if it is 5.8G, it will include 5.725G~5.85G in China.
If it is only for UAV applications, it is useless if the frequency band is too wide, but if the frequency band of the antenna is too narrow, it will affect the use of the channel.
In summary, for non-video transmission drones such as model aircraft, you can choose some lower frequency bands, which have strong diffraction capabilities and long transmission distances; for video transmission drones, it is best to choose 2.4G and 5G with high channel bandwidth. Which frequency band mainly depends on the surrounding natural environment and the usage of the corresponding channel to avoid interference sources; then, according to the actual demand, install an antenna of a suitable size.
In the home environment, generally, 2.4G has a lot of interference and 5.8G has less interference. The main reason is that 2.4G has a strong transmission capacity. The poor 5.8G transmission capacity has been lost.
Besides the How To Choose 2.4G And 5G article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G