What is the LoRaNET?
LoRaNET is a LoRa networking protocol that supports secondary development, LoRaNet SDK uses an AMetal software platform, it provides some basic components, which provides a good abstraction of most on-chip hardware resources, when using peripherals, you only need to simply configure, call API, no need to pay attention to the underlying hardware operation.
What are LoRaNET Features?
LoRaNET uses LoRa spread spectrum modulation technology to achieve low transmit power long-distance communication.
Basic packet sending and receiving modes: unicast, multicast, broadcast.
Address width 16bits; (now you don’t have to worry about not having enough node addresses)
A communication rate of 0.3-19.2kbps can be set, and the coding rate is adjustable.
A low-power wake-up mechanism, interval opening reception.
Each packet can carry 210 bytes of data, supporting 4 levels of the relay.
What kind of network is LoRaNET?
LoRaNET protocol has different networking modes according to different application scenarios, and there are 3 main networking modes as follows.
1. Data collection type application
This is a star-shaped network consisting of concentrators, a small number of routes, and a large number of terminals, as shown in the following figure.
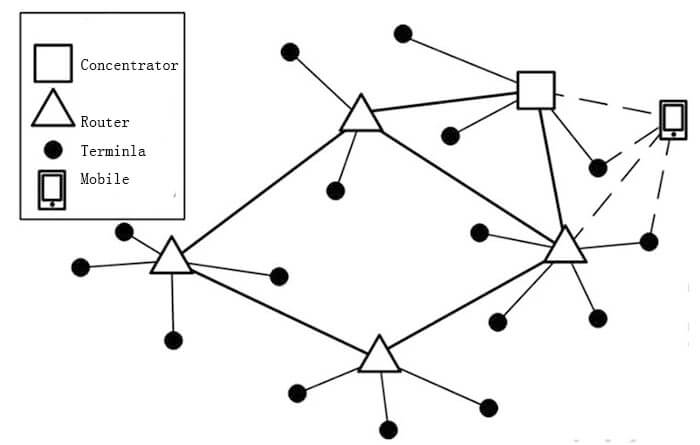
Figure 1 LoRaNET data collection network
The characteristics of this type of network are as follows.
Automatic detection of network formation
Acquisition commands are initiated by the concentrator with polled acquisition and grouped batch acquisition
Use of fixed tree routing, requiring fixed relative positions between nodes
Since all data collection is initiated by the concentrator, it is suitable for occasions with low real-time requirements
To summarize: routing, concentrator-initiated collection, relatively fixed node location, low real-time
2. Burst reporting type application
Star network is composed of concentrators and terminals, with the following characteristics.
Support for auto-detection networking, without support for routing.
Active reporting from the terminal to the concentrator, which is suitable for applications with high real-time requirements.
Using an acknowledgment response mechanism, which automatically retransmits when a packet is lost until success or timeout.
Failure retransmission mechanism includes a channel conflict avoidance mechanism to avoid network blocking.
Use two channels for data transmission and reply packet transmission respectively.
To summarize: no routing, terminal active reporting, data transmission packet loss retransmission, high real-time.
3. Time-sharing reporting type application
A network composed of concentrators and terminals with the following characteristics.
Support auto-detection networking, no routing.
Allowing configuration of the reporting time, the concentrator can initiate a timed broadcast to keep the devices in the network in time synchronization.
(b) Each terminal reports data at the designated reporting time in a time-sharing manner.
Less over-the-air wake-up calls, which can be used for low-rate long-distance communication occasions.
To sum up: no routing, terminal time-sharing reporting, data transmission packet loss retransmission, or concentrator broadcast to keep time synchronization.
4. What do the devices in the LoRaNET network do?
Concentrator
The concentrator is the entry point of the network and plays the role of a gateway. Usually, communication commands are initiated by the concentrator, and terminals and routes respond passively to these communication commands.
Terminal
Terminal devices are the devices that are controlled and data collected in LoRaNET, and they form a star network with concentrators or routers.
Routing
Routing is responsible for forwarding data packets and determining the forwarding path based on the routing information carried in the data packets
5. How is the network of LoRaNET actually organized?
The routing table information in LoRaNET is stored in the concentrator and the so-called networking is the process of determining the network topology. After networking, the concentrator can access any end node in the network. There are 2 types of networking.
Auto-detection networking
The network is initiated by the concentrator, which detects the surrounding routes and terminals and adds the topological relationship of each node to the routing table.
Editing routing information method
The API is called to add the routing information into the routing table in order.
6. How to use LoRaNET?
You just need a zip package, unzip it and click it to use it directly.
LoRaNET Transparent Transmission Module is embedded with self-grouping transparent transmission protocol, supporting users to self-grouping with one click, and providing dedicated meter reading protocol, CLAA protocol, and LoRaWAN protocol, users can develop applications directly without spending a lot of time on the protocol.
Besides the What is LoRaNET article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G