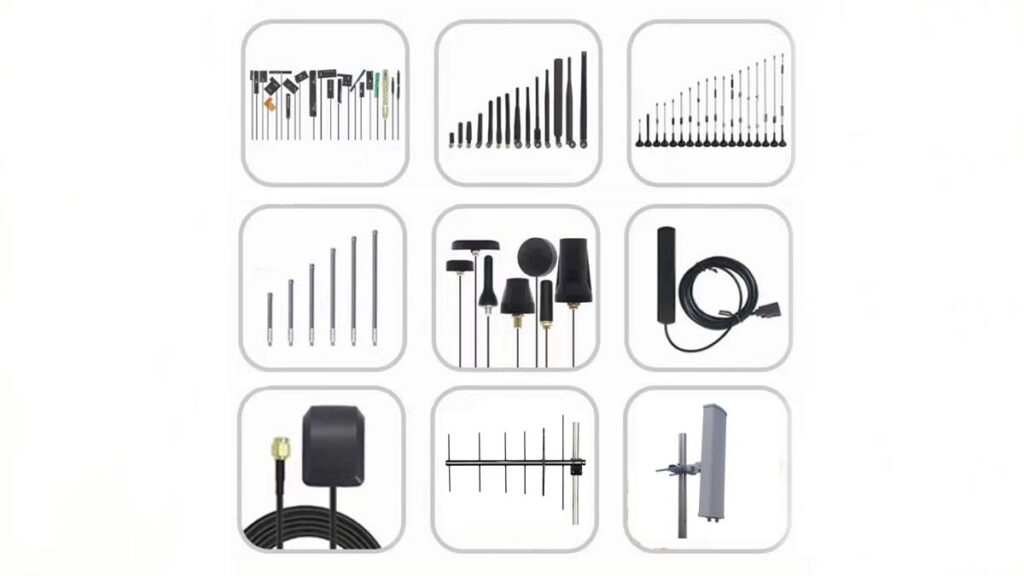
The antenna selection guide for RF applications is telling you how to choose the right antenna for your radio frequency applications.
Many hardware engineers, system engineers, or test engineers will need to use the antenna when making products.
When choosing an antenna, you need to consider the signal frequency, gain, directionality, shape, size, material, environment, RF interface, chip design, and other factors. Considering the above factors comprehensively, determine the antenna scheme suitable for specific application scenarios, to achieve the purpose of optimization.
What is an antenna?
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and the electric current moving through a metallic conductor, used in conjunction with a transmitter or receiver.
During transmission, the radio transmitter supplies current to the terminals of the antenna, and the antenna radiates the energy in the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves).
During reception, the antenna intercepts some of the energy of the radio waves to generate a current at its terminals, which is applied to the receiver for amplification. Antennas are an important part of all radio equipment.
What type of antenna can choose?
The distinguishing factor of antennas is how they send signals. Either the signal radiates in every direction, called an omnidirectional antenna, or there is a reflective surface that focuses the signal in a specific direction, called a directional antenna.
Depending on the main application, there are ceiling antennas, panel antennas, Yagi antennas, omnidirectional antennas, and rubber duck antennas. These antennas operate at different frequencies and gains, depending on whether they radiate signals in the omnidirectional or directional range.

What types of antennas are available?
There are many types of antennas, which can be classified into the following broad categories according to the applications.
- TV antenna: The antenna used to receive TV signals, common indoors and outdoors two kinds.
- Mobile phone antenna: The antenna used for mobile phone communication, data transmission and positioning, common patch antenna, PIFA antenna, PCB antenna, and so on.
- Wireless network antenna: The antenna used for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other wireless network signals, common directional antenna, gain antenna, omnidirectional antenna, and so on.
- Satellite communication antenna: The antenna used for a satellite communication system, common plane antenna, parabolic antenna, microstrip antenna, etc.
What are the common types of engineering equipment antennas?
(1) Flat plate antenna: high efficiency, lightweight, and easy to install, can take into account the gain and radiation area. Suitable for indoor, tunnel wireless signal coverage, medium distance signal transmission, map transmission and signal through the wall.
(2) Yagi antenna: very high gain, slightly larger size, strong directionality, need to pay attention to the direction of the antenna, can be used for ultra-long-distance signal transmission, mapping, and direction finding.
(3) Log Periodic Antenna: ultra-wideband antenna, bandwidth coverage is very wide, bandwidth up to 10:1, commonly used in signal amplification, indoor distribution, and lift signal coverage.
4) Magnetic mount antenna: relatively high gain, the most important feature is with strong magnetic base mount, it is very convenient to install and fix, but the magnetic base mount must be adsorbed on the metal surface.
In the wireless module industry, the magnetic base mount antenna is often used in conjunction with the wireless module, to achieve the purpose of increasing the communication distance of the wireless module, such as intelligent meter reading, vending machines, express cabinets, car radios, and so on.
(5) Rubber duck antenna: it is the most common external antenna, with moderate gain and relatively low price, commonly used in wireless communication modules, wireless routing, digital transmission radio, etc. The size can be selected according to the installation space requirement.
According to the installation space requirements to choose the appropriate size of the antenna, select the antenna size and gain has a relationship, usually, the same band length the longer the higher the gain.
(6) PCB antenna: the biggest difference between an FPC antenna and a PCB antenna is that FPC has good flexibility, A PCB antenna is a hard board, in the structure of the installation, if you need to bend and curve surface, choose an FPC antenna if it is a flat surface PCB antenna, PCB antenna is easier to install than FPC.
The role of the antenna is to radiate the RF signal into the free space, this time choosing the right antenna for the transmission distance has a great impact. The antenna is very sensitive to the surrounding environment, and in many cases, it will appear that even if you choose the right antenna, you can’t achieve the expected results.
The antenna selection guides
The types of antennas are very many, according to different needs, the antenna required is not the same. It is important to understand the characteristics of the different parameters of the antenna so that you can choose the right antenna for your engineering equipment.
How to choose the right antenna?
The antenna selection guide for how to choose antenna by parameter explanation.
Antenna Selection Guide 1. Antenna frequency range
Different application scenarios require different frequency ranges of the antenna, so when choosing an antenna, we should choose the appropriate frequency range according to the specific application.
For example, WIFI antenna, we choose a 2.4GHz-2.483GHz range of antennas, where the range generally refers to the range of S11 ≤ -10dB;
Antenna Selection Guide 2. Antenna size
Antenna size on the signal transmission ability will also have an impact, generally speaking, the larger the antenna size, the stronger the transmission ability, but will also bring more weight and volume, affecting the carrying and installation.
For example, external antenna we can choose a glass steel antenna, yagi antenna, and other finished products, For a built-in antenna can choose a flexible PCB and PCB antenna, microstrip antenna, ceramic antenna, and so on;
Antenna Selection Guide 3. Antenna directionality
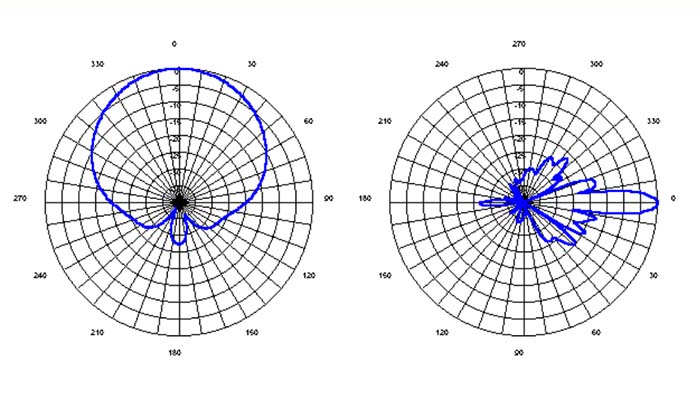
The choice of antenna directionality means to choose a directional antenna or omnidirectional antenna; a directional antenna in one direction gain is very light, the other direction gain is very soft, the omnidirectional antenna in any direction has almost the same gain; for example:
Directional map of the goodwill directly may affect our practical, for example, if I choose an omnidirectional antenna, I hope it has a better radiation gain in each direction, but due to the antenna installation environment or the antenna itself directional map of the defects will affect our use, in the long-distance limit may be certain directions to receive or receive no signal;
Antenna Selection Guide 4. Antenna gain
Gain is the antenna receiving, and transmitting signal ability to measure the index, the higher the gain antenna transmission distance is, but at the same time will also bring more noise interference. The selection of antennas should be based on the actual needs of reasonable choice.
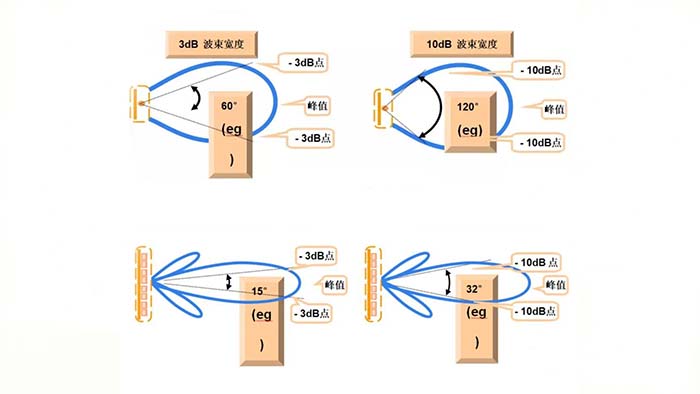
The size of the gain directly affects the whole communication link budget (communication distance), but usually, the antenna gives the gain is the direction of the maximum direction of the gain (unit dBi), and does not represent all the directions of the gain, so generally omnidirectional antenna can also understand the following degree of incompleteness, directional antenna can be understood as follows the sub-flap level and before and after the ratio of these indicators;
According to the theory and test experience, the general definition of the link budget is less than 6dB, the communication distance is halved, such as a pair of 2.4GHz wireless module link budget is 100dB (plus antenna gain), the communication distance is 1km, then 94dB link budget, the communication distance is 500m;
Antenna Selection Guide 5. Antenna material
Antenna material is generally the material of the antenna itself and the material of the shell, the material of the common microstrip PCB antenna, FPC antenna, copper antenna, metal sheet antenna, copper tube antenna, spring coil antenna, and so on;
Antenna Selection Guide 6. Antenna connector
Antenna connector generally refers to the antenna port connector form, such as IPEX, SMA, N-type, TNC, BNC, TS9, MMXC, Fakra, and so on.
Antenna Selection Guide 7. VSWR
VSWR is defined as the amplitude ratio of standing wave belly voltage and valley voltage it can be regarded as the antenna port reflection size, VSWR is equal to 1, which means that the feed line and antenna impedance are completely matched, at this time, all the high-frequency energy into the antenna is converted to radiate out, there is no energy loss of reflection;
VSWR for infinity said the whole reflection, energy is not radiated out; general antenna requirements in the case of ensuring other characteristics of the antenna, VSWR ≤ 2 (S11 ≤ -10dB) for the determination of the conditions, VSWR = 2, at this time, about 10% of the reflected energy, 90% of the energy into the antenna;
Antenna Selection Guide 8. Antenna impedance
Antenna port impedance is a complex number (R + jX), we say that the antenna port impedance is 50 Ω, the ideal case of the virtual part of the 0, but in fact, the frequency range can not be all 0, so there must be reflection;
In fact, VSWR disguised as input impedance VSWR = ( Zi-50)/( Zi + 50);
Antenna Selection Guide 9. Antenna polarisation mode
Antennas mainly have line polarisation (vertical polarisation and horizontal polarisation), circular polarisation (right-handed circular polarisation and left-handed circular polarisation), and elliptical polarisation points, general line polarization is mostly, common copper tube antennas, FPC antennas, dipole antennas, and Yagi antennas and so on belong to the line polarisation antenna;
Common GPS antennas, spring antennas, helical antennas, etc. belong to circularly polarised antennas;
The main parameters of antennas are frequency range, gain, antenna material, antenna connector, VSWR, impedance, polarisation mode, directionality, physical dimensions, maximum power, etc.; We have to find the most suitable antenna according to our needs requirements.
Choosing the right antenna is an important guarantee to guarantee the signal transmission and reception of our electronic devices. Through the introduction and analysis of antenna types, application scenarios, and precautions, we believe that we can better choose the right antenna for ourselves and make our lives more convenient and intelligent.
Besides this Antenna Selection Guide For RF Applications article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G