Global System for Mobile Communications, or GSM for short, is a digital mobile communications standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Organization ETSI. It uses time division multiple access technologies for its air interface. Since its commercial introduction in the mid-1990s, it has been adopted by more than 100 countries worldwide.
GSM is an open standard currently being developed by 3GPP. 2015, many GSM networks are used by operators worldwide.
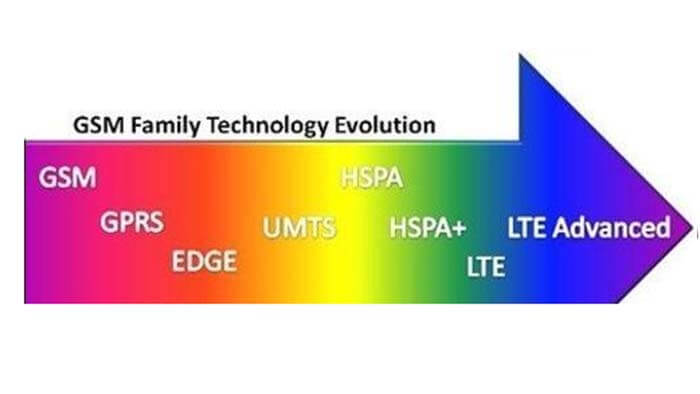
GSM belongs to the 2nd generation (2G) cellular mobile communication technology. Analog cellular technology is known as Generation 1 mobile technology, and broadband CDMA technology is known as Generation 3 mobile technology, or 3G.
GSM is a digital cell phone network standard developed in Europe to allow users to use one cell phone network standard for all parts of the world so that users can travel around the world with one cell phone.
What is GSM system?
The GSM system includes the GSM 900: 900MHz, GSM 1800: 1800MHz, and GSM-1900, 1900MHz bands.
What is GSM band?
When it comes to the frequency bands supported by cell phones, it should be clear that the frequency bands are essentially rigidly divided, mainly due to the limited frequency resources, and the Ministry of Information Industry is currently responsible for related matters.
China’s cell phones commonly used frequency bands are CDMA cell phones occupy the CDMA1X, 800MHz band; GSM cell phones occupy the 900/1800MHz band; the last two years of GSM1X dual-mode occupy the 900/1800MHZ band; 3G occupy the 1900/2000/2100MHz band.
What is GSM dual-band?
China’s GSM cell phones occupy the frequency band is mainly 900MHZ and 1800MHZ.
Using GSM900/GSM1800 dual-band cell phones, users can switch freely between GSM900 and GSM1800, which can effectively avoid the previous problems of dropped calls, difficult calls, and poor sound quality, which is more convenient than the previous calls using only the GSM900 network.
What is GSM tri-band?
The so-called “tri-band” means that it contains three operating frequencies, which are GSM900Mhz, DCS1800Mhz, and PCS1900Mhz.
A tri-band phone means that the phone can receive signals from GSM900M, DCS1800Mhz, and PCS1900Mhz at the same time, and choose the signal of the base station if the signal of that band is strong, or switch to another band if one of them does not work.
It actually expands the connection rate of cell phones. The PCS1900 megahertz network is the most popular network in North America (USA, Canada) and Europe.
Since tri-band phones can work in three different frequency bands at the same time, tri-band phones undoubtedly have the characteristics of all three networks.
From a technical point of view, GSM1800 has good signal penetration because of its high-frequency band, thus providing good call quality and coverage in complex environments with tall buildings, while PCS1900 has good communication capabilities in North America (USA, Canada) and Europe, which undoubtedly provides the service needed by those who travel frequently between continents.
What is GSM Radio Interface?
GSM is a cellular network, which means that a cell phone is connected to the nearest cellular area that it can search.
There are four different cell sizes in GSM networks: giant cell, microcell, pico-cell, and umbrella cell. The coverage area varies depending on the environment. A giant cell can be thought of as a base station antenna mounted on a mast or on top of a building.
Microcells are those with antenna heights below the average building height and are generally used in urban areas. Microcells are very small cells that cover only a few tens of meters and are mainly used indoors.
Umbrella cells are used to cover the blind spots of smaller cellular networks and fill the signal gap between cells.
Cell radius can range from over a hundred meters to tens of kilometers depending on antenna height, gain, and propagation conditions. The longest distance in actual use is supported by the GSM specification up to 35 km.
There is also a concept of extended cellularity, where the cellular radius can be doubled or more.
GSM also supports indoor coverage, where the power from the outdoor antenna can be distributed to the indoor antenna distribution system via a power divider.
This is a typical configuration to meet indoor high-density call requirements and is common in shopping malls and airports. This is not necessary, however, as indoor coverage can also be achieved by passing the radio signal through buildings, only this improves signal quality and reduces interference and echoes.
What is GSM's main technical feature?
Spectral efficiency
The system is spectrally efficient due to the use of efficient modulators, channel coding, interleaving, equalization, and voice coding techniques.
Capacity
The GSM system can be reduced to 4/12 or 3/9 or even smaller (7/21 for analog systems) due to the increased transmission bandwidth per channel, which reduces the co-channel multiplexing plant ratio requirement to 9 dB.
Voice quality
Due to the characteristics of digital transmission technology and the definition of the air interface and voice coding in the GSM specification, the voice quality always reaches the same level above the threshold value independent of the radio transmission quality.
Open interfaces
The open interfaces provided by the GSM standard are not only limited to the air interface, but also between networks and between the various device entities in the network, e.g. the A and Abis interfaces.
Security
Security is achieved through authentication, encryption, and the use of TMSI numbers. Authentication is used to verify the user’s right to access the network. Encryption is used for the air interface and is determined by the key of the SIM card and the network AUC. TMSI is a temporary identification number assigned to the subscriber by the service network to prevent someone from tracking and revealing his or her geographic location.
Interconnection with ISDN, PSTN, etc.
Interconnection with other networks usually utilizes existing interfaces, such as ISUP or TUP.
Roaming on the basis of SIM card
Roaming is an important feature of mobile communications, marking the automatic access of users from one network to another. GSM systems can provide global roaming, but of course, certain agreements between network operators, such as billing, are also required.
Besides the What is GSM meaning article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G