This article clarifies the key the difference between NB-IoT and CAT-M1, and their use cases.
NB-IoT and Cat M1 technology are two popular IoT connectivity options today. Understanding the differences and use cases is important to find the right technology to support a specific use case.
The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) technology over the past few years is well documented, with experts predicting that the number of IoT devices will reach 75 billion. To drive this trend, project managers and developers look for IoT devices that support the specific range, bandwidth, and data loads they need to cover to enable them to bring their innovative ideas to market successfully.
Technically, any connection can do the job, but choosing the perfect IoT solution for your project can lead to improved quality of service, cost savings, and operations, so start by understanding the difference between NB-IoT and CAT-M1.
What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things or NB1)
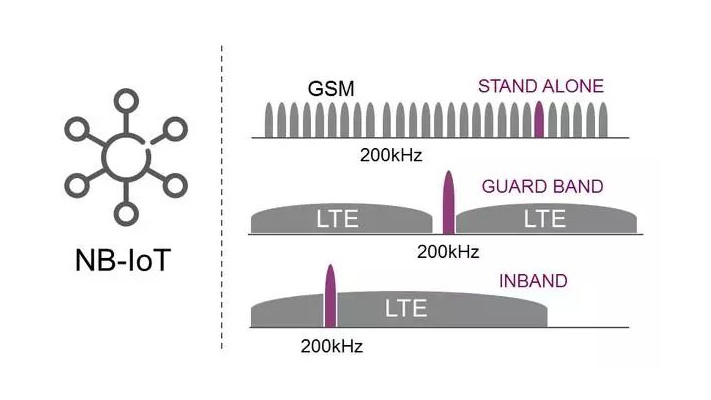
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) technology operates using blocks of spectrum resources in existing LTE networks or LTE carrier-protected bands. It can also use spectrum in the 200 kHz bandwidth previously used by GSM but not currently in use.
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things or NB1) is another new mobile data standard for the growing low-power wireless applications (LPWA) market. NB-IoT has uplink speeds of 66 kbps and download speeds of 26 kbps in half-duplex mode, which means that data travels in one direction at a time. It also has a latency of 1.6 to 10 seconds.
It operates at a bandwidth of 180 kHz and can be deployed in the protected band portion of the LTE network, which is between channels in the unused portion of the spectrum. As a result, it excels in IoT projects that cover a wide range of areas, offering an impressive seven times the current technology such as CAT M1. Narrowband IoT offers better building and obstacle protection.
NB-IoT relies on simple waveforms for connectivity and consumes very little power compared to LTE Cat M1. As a result, NB-IoT devices provide better building and obstacle penetration. This also means NB-IoT devices cannot send as much data as LTE Cat M1.
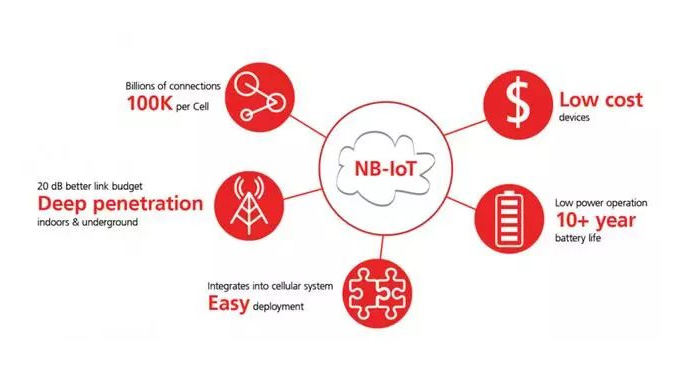
NB-IoT Use Cases
The most common use cases for NB-IoT include smart gas, water, and electric meters, smart city applications such as smart street lights and parking sensors, and other remote sensing applications that don’t send data frequently or in large amounts.
These include HVAC controls, industrial monitors, and agricultural sensors that monitor irrigation systems and detect leaks.
What is Cat-M1(LTE-M)?
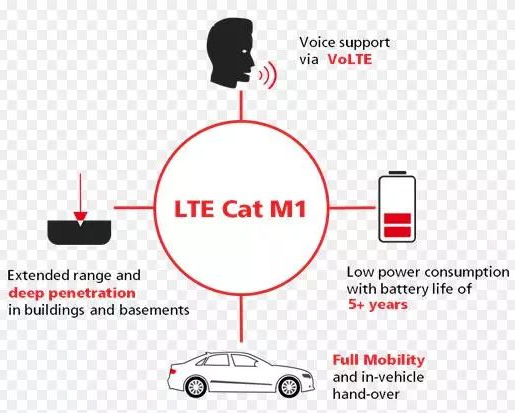
Cat-M1/ LTE Cat-M
LTE-M (LTE Cat-M or Cat-M1) is a new mobile data standard for the growing Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) market. It is best suited for transmitting low-to-medium data over a long range.
LTECat M1 is a new low-power wide area (LPWA, low-power wide-area) cellular technology specifically designed for Internet of Things (loT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.
It has been developed for low- to medium-data-rate applications that support upload and download data rates below 1 Mbps and can be used in either half-or full-duplex mode.
LTE CATM1 operates using existing LTE networks, but unlike NB-IoT (which operates using unused spectrum or spectrum located in protected bands) LTECATM1 operates in the same LTE frequency bands used for cellular applications.
One of its advantages is that it can switch from one cell site to another, which allows the use of the technology in mobile applications;
The NB-IoT, on the other hand, does not allow mobile switching from one cell site to another, and can therefore only be used in fixed applications, i.e., applications that are limited to the area covered by a single cell site.
Since LTE Cat M1 technology can coexist with 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks, it has the advantage of all the security and privacy features of a mobile network, such as support for user identity confidentiality, entity authentication, secrecy, data integrity, and the ability to authenticate mobile devices.
Cat-M1 provides fast enough bandwidth that it differs from NB-IoT in several other ways:
Cat-M1 supports cell tower switching, so it works with mobile applications such as asset tracking and fleet management. It also supports voice capabilities in IoT applications, such as medical alert devices and home alarm systems.
The standard, which uses 1.4MHz of bandwidth, also has enough throughput to transmit firmware, software, and other security updates to IoT devices, including a full Linux operating system-something NB-IoT can’t do.
Additionally, Cat-M1 supports both full and half duplex, which means organizations can reduce power consumption and increase battery life by opting for half duplex. It’s faster, with upload and download speeds of 1Mbps and lower latency of 10 to 15 milliseconds.
Cat-M1 Use Cases
The most common use cases for Cat-M1include wearable devices such as fitness bands, smartwatches, automated teller machines (ATMs), asset tracking, health monitors, and alarms.
It is also widely used in metering applications, security monitoring, building surveillance
systems, and telematics.
It also has some crossover with NB-IoT to work with smart meters and industrial monitor.
So, what is the difference between NB-IoT and Cat-M1?
Based on the definition of 3GPP Release 13, the following table compares the key specifications of NB-IOT with LTE CAT-M1.
| Spec | LTE Cat M1 | NB-IoT |
| Deployment | In-Band LTE | In-Band LTE,LTE Guard Bands, Standalone |
| Downlink Modulation | OFDMA, 16 QAM | OFDMA |
| Downlimk Datarate | Up to 1 Mbps | 250 kbps |
| Uplink Modulation | SC-FDMA, 16 QAM | SC-FDMA |
| Uplink Datarate | Up to 1 Mbps | 250
kbps (multi-tone), 20 kbps (single tone) |
| Bandwidth | 1.08 MHz | 180 khz |
| Duplexing Technology |
Full
Duplex, Half Duplex, FDD& TDD |
Half Duplex and FDD |
| Latency | 10 to 15 milli seconds | 1.6to 10 seconds |
| Link Budget | 155.7dB | 164 dB |
| Power Class | 23 dBm, 20 dBm | 23 dBm, 20 dBm |
The difference use cases between NB-IoT and Cat-M1
| Applications | NB-IoT | LTE-M |
| Smart City | Static applications with low bandwidth requirements, such as smart parking, noise, pollution monitoring, waste management and smart traffic monitoring. | Applications with substantial downlink requirements and/or voice support, such as street lighting, traffic management, panic buttons, and SOS stations with optional voice support. |
| Intelligent Agriculture | Stationary applications with low bandwidth requirements, such as weather stations, soil moisture/temperature and humidity levels, and other environmental applications. | Applications with substantial downlink requirements and/or mobility, such as smart irrigation, HVAC control in animal houses, and live animal tracking. |
| Logistics & Transportation | Semi-fixed assets such as commercial refrigeration equipment (ice cream, beverages, etc.) and on-site logistics equipment (shelving, carts, lifts and other warehouse machinery). | Personal tracking applications (cars, bikes, pets, children), fleet monitoring (especially trucks), and non-fixed assets such as logistics equipment (cargo, crates, pallets, etc.). |
| Industry & Manufacturing | Stationary machinery with low data rates for process variables indirectly affecting yield and quality, industrial assettracking, and energy monitoring. | Machines with higher bandwidth requirements for process variables that directly affect production or quality, IoT gateways connected to PLCs for tag monitoring and worker monitoring. |
Besides this What is the Difference Between NB-IoT And Cat-M1 article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
PCB Antenna VS. External Antenna
Ceramic Antenna VS. PCB Antenna, A Comparison Guide
Wifi vs. 5G, is 5G better than Wifi?
Mobile Networks’ Evolution From 1G To 5G
How To Choose Embedded Antenna For IoT?